The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, consists of twelve lunar months, each with unique significance and characteristics. The months are:
1: Muharram

(forbidden) – A sacred month where fighting is prohibited, including the observance of ‘Āshūrā’.
2: Safar

(void) – Named for the emptiness of pre-Islamic Arab homes during this time.
3:Rabī‘ al-awwal

(the first spring) – Celebrated for the birth of Prophet Muhammad.
4:Rabī‘ ath-thānī

(the second spring) – Continues the theme of spring.
5: Jumādá al-ūlá

(the first of parched land) – Associated with dry conditions.
6: Jumādá al-ākhirah

(the last of parched land) – Completes the dry season.
7: Rajab

(respect) – Another sacred month where fighting is also forbidden.
8: Sha‘bān

(scattered) – Marks the time when tribes would disperse to find water.
9: Ramaḍān
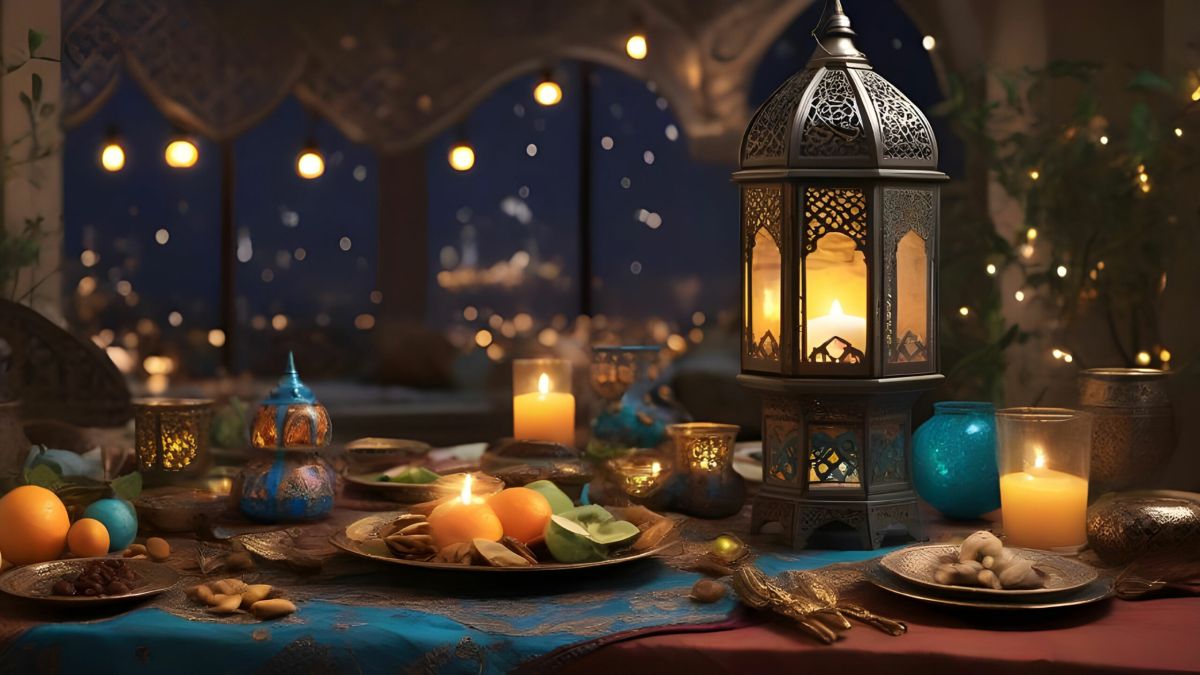

(burning heat) – The holy month of fasting from dawn to sunset, emphasizing spiritual reflection and charity.
10: Shawwāl

(raised) – Begins with Eid al-Fitr, celebrating the end of Ramadan.
11: Dhū al-Qa‘dah

(the one of sitting) – A month where warfare is traditionally suspended.
12: Dhū al-Ḥijjah

(the one of pilgrimage) – The month of Hajj, where millions gather in Mecca for pilgrimage rituals.